Usability is a key component of the User Centered Design approach as a quality attribute that assesses how easy user interfaces are to use. Usability can be defined by 5 quality components (Jakob Nielsen):
- Learnability
- Efficiency
- Memorability
- Satisfaction
- Errors
How easy is it for users to accomplish basic tasks the first time they encounter the design? how much do users have the think!
Once users have learned the design, how quickly can they perform the same and new tasks?
Why?
Usability is a necessary condition for product success. If a website, app, or service is difficult to use, people will seek alternatives. Current best practices call for spending about 10% of a design project's budget on usability. On average, this will more than double a products desired quality metrics. Usability can also help cut training budgets and increase productivity. Essentially Usability leads to increased sales, registered users, customer leads, or whatever desired goal motivated the design project.
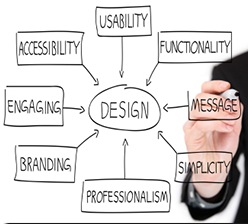
What?
There are several methods for studying usability including:

can be face-to-face or via phone/skype etc. Follows a script and often used to gather stakeholder of specialist feedback
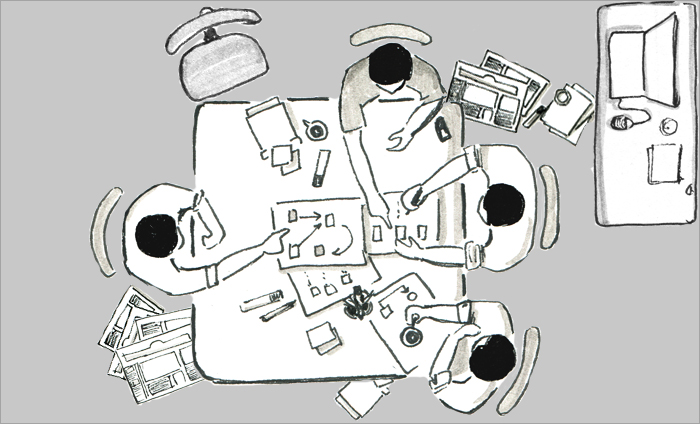 involves collaberative working with groups of users to generate or critique design ideas and solutions
involves collaberative working with groups of users to generate or critique design ideas and solutions targeted uses are guided/observed performing key scenarios/tasks to validate & test designs at various stages of development
targeted uses are guided/observed performing key scenarios/tasks to validate & test designs at various stages of development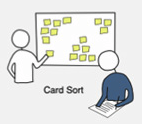 method for increasing a system’s findability. Used to help design or evaluate the information architecture. Participants organize & prioritise topics or features
method for increasing a system’s findability. Used to help design or evaluate the information architecture. Participants organize & prioritise topics or features looking for patterns in quantitative test data such as eye tracking, heat maps, task errors, time or clicks to complete, and physiological (biometric) data to detect emotional response especially with video games user testing
looking for patterns in quantitative test data such as eye tracking, heat maps, task errors, time or clicks to complete, and physiological (biometric) data to detect emotional response especially with video games user testingWhen
 Usability plays a key role in each stage of the UX design process. Iterative design is the best way to increase the quality of user experience. It is often better to run many small tests and revise the design between each one.
Usability plays a key role in each stage of the UX design process. Iterative design is the best way to increase the quality of user experience. It is often better to run many small tests and revise the design between each one.
Where
 Testing can be performed in a dedicated usability laboratory, or in a more ad-hoc way using a quiet space. It will depend on the number and complexity of the testing involved. What matters is getting hold of real users and sitting/observing them while they interact with the design.
Testing can be performed in a dedicated usability laboratory, or in a more ad-hoc way using a quiet space. It will depend on the number and complexity of the testing involved. What matters is getting hold of real users and sitting/observing them while they interact with the design.
How

To identify most important usability problems, testing 5-8 users is typically enough. The test methodology will relate to the design objectives, and careful selection/screening of target participants is necessary to avoid skewing test data, ensuring the UX findings are addressing the target audience.




